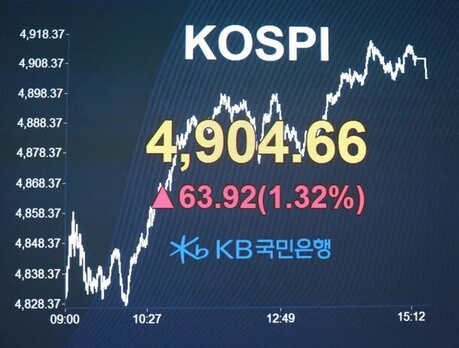
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC), the world's leading contract chip manufacturer, has sent ripples of excitement throughout the technology sector with the unveiling of its cutting-edge 2-nanometer (nm) chip.
TSMC is slated to commence mass production of these revolutionary 2nm chips in the latter half of this year. This development is widely regarded as a monumental leap forward in both performance and efficiency, holding the potential to fundamentally reshape the technological landscape.
Microchips serve as the bedrock of modern technology, powering virtually every electronic device from electric toothbrushes and smartphones to laptops and household appliances. These intricate components are constructed by layering materials like silicon and etching ultra-fine circuits, ultimately housing billions of transistors within a single die.
Transistors act as minuscule electrical switches, controlling the flow of electricity and forming the essential building blocks for computer operations. As a general rule, a higher density of transistors on a chip translates to enhanced processing speeds and overall performance.
The semiconductor industry has been in a constant pursuit of shrinking transistor sizes to pack more onto a single chip. This relentless drive has fueled the creation of faster, more powerful, and increasingly energy-efficient electronic devices.
TSMC's novel 2nm technology is anticipated to deliver substantial advantages over its predecessor, the industry-leading 3nm chip. It is projected to achieve a 10-15% increase in computing speed at the same power level or a 20-30% reduction in power consumption while maintaining equivalent performance.
Furthermore, the transistor density of the 2nm chip has increased by approximately 15% compared to the 3nm technology. This enhanced density will empower electronic devices to operate at faster speeds, consume less energy, and handle more complex tasks with greater efficiency.
Further Insights:
Nanometer (nm) Process: A unit of measurement defining the linewidth of circuits on a semiconductor chip. A smaller number indicates a finer linewidth, allowing for a greater number of transistors to be packed into a smaller area. This miniaturization leads to improved chip performance, increased power efficiency, and a reduction in chip size. The 2nm process represents the most advanced semiconductor manufacturing technology achieved to date.
TSMC (Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company): The world's largest dedicated independent semiconductor foundry, manufacturing chips designed by fabless companies. TSMC is a global leader in advanced process technologies and plays a pivotal role in the global IT industry.
Transistor Density: The number of transistors integrated within a specific area of a semiconductor chip. Higher transistor density generally correlates with improved chip performance and efficiency. The 2nm process leverages advanced manufacturing techniques, including Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) lithography, to achieve its high transistor density.
AI Revolution: The ongoing era of profound and transformative changes across society driven by advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology. High-performance semiconductors like the 2nm chip provide the essential foundational technology for efficiently processing the complex computations required by AI algorithms.
Silicon Shield: A metaphorical term used to describe the critical importance of Taiwan's semiconductor industry to the global economy. It suggests that Taiwan's advanced chip manufacturing capabilities could act as a deterrent against potential military aggression.
Foundry: A company that specializes in manufacturing semiconductors for other companies that design them. TSMC is a prime example of a foundry.
Fabless: A company that specializes in designing semiconductors but does not own or operate its own manufacturing facilities. Qualcomm, NVIDIA, and Apple are prominent examples of fabless companies.
EUV Lithography (Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography): A cutting-edge lithography technology that uses extremely short wavelengths of light to create the intricate patterns on semiconductor wafers, enabling the production of smaller and more powerful chips.
The development of TSMC's 2nm chip is poised to catalyze transformative advancements across a wide spectrum of fields, including artificial intelligence, high-performance computing, and mobile devices. Notably, it is expected to serve as a crucial enabler for the progression of AI technologies, which demand immense computational power. Simultaneously, this breakthrough will further solidify Taiwan's technological prowess within the global semiconductor supply chain and reinforce its role as a "silicon shield" amidst geopolitical tensions. The enhanced capabilities offered by 2nm chips will likely pave the way for a new generation of electronic devices with unprecedented performance and energy efficiency, ushering in a new era of technological innovation.
[Copyright (c) Global Economic Times. All Rights Reserved.]