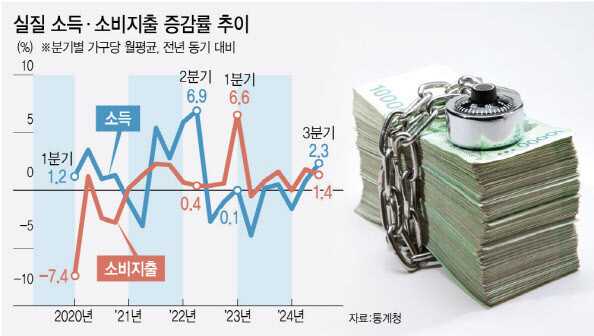
Seoul, South Korea – South Korea's households experienced a boost in both income and savings in the third quarter of 2024, according to data released by the Statistics Korea on November 28th.
The average monthly household income increased by 4.4% year-on-year to 5,255,000 won, and real disposable income, adjusted for inflation, grew by 2.3%. This marks the second consecutive quarter of real income growth.
The increase in household income was primarily driven by a rise in employment and wages. Average monthly earnings from employment rose by 3.3% to 3,329,000 won.
Despite the overall positive trend, income inequality widened. While the top 20% of households enjoyed a significant increase in income, mainly from employment, the bottom 20% saw a decline in employment income, relying more on social benefits and pensions.
Key findings from the report include:
Rising household income: Average monthly household income increased by 4.4% year-on-year.
Strong labor market: Employment and wages contributed significantly to the overall income growth.
Increasing savings: Household savings rate rose to 30.6%, the highest in nine quarters.
Widening income inequality: The income gap between the top and bottom 20% of households continued to widen.
The government has attributed the positive economic indicators to various factors, including increased employment and wage growth. However, it also acknowledged the growing income inequality and pledged to continue efforts to create more jobs, stabilize prices, and support vulnerable groups.
[Copyright (c) Global Economic Times. All Rights Reserved.]





























