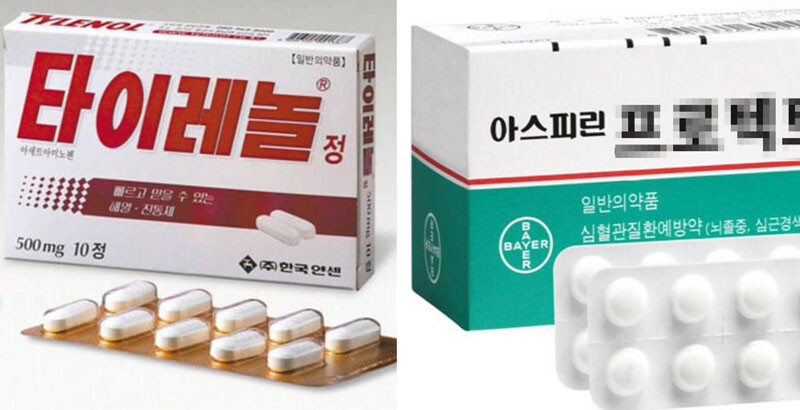
Both Tylenol and aspirin are widely used over-the-counter pain relievers, but they differ significantly in their mechanisms of action, effects, and side effects.
Active Ingredients and Mechanisms of Action Tylenol contains acetaminophen, which works by blocking pain signals in the brain. It is primarily used to reduce fever and relieve pain, but it does not have anti-inflammatory properties. Aspirin, on the other hand, contains salicylic acid, which inhibits blood clotting and reduces inflammation. As a result, it can alleviate pain, reduce fever, and decrease inflammation.
Effects Tylenol is effective for relieving headaches, menstrual cramps, and muscle aches. It is also a potent fever reducer. Aspirin, similarly, can alleviate headaches and menstrual cramps. Additionally, it is effective for treating inflammatory conditions such as arthritis and is often prescribed in low doses for long-term use to prevent cardiovascular disease.
Side Effects Overdosing on Tylenol can lead to liver damage, so it should be used with caution by individuals with liver disease. Aspirin can irritate the stomach and increase the risk of bleeding. People with aspirin allergies should avoid taking it.
Precautions Individuals with liver impairment and pregnant women should consult a healthcare professional before taking Tylenol. Aspirin should be used with caution by people with ulcers, bleeding disorders, and pregnant women.
Which one should you choose?
For simple headaches or menstrual cramps: Both Tylenol and aspirin can be effective.
For pain accompanied by inflammation: Aspirin is more effective.
For preventing cardiovascular disease: Low-dose aspirin may be prescribed. However, consult a healthcare professional before starting any new medication.
If you are unsure about which pain reliever is right for you, it is always best to consult with a pharmacist or healthcare provider.
[Copyright (c) Global Economic Times. All Rights Reserved.]