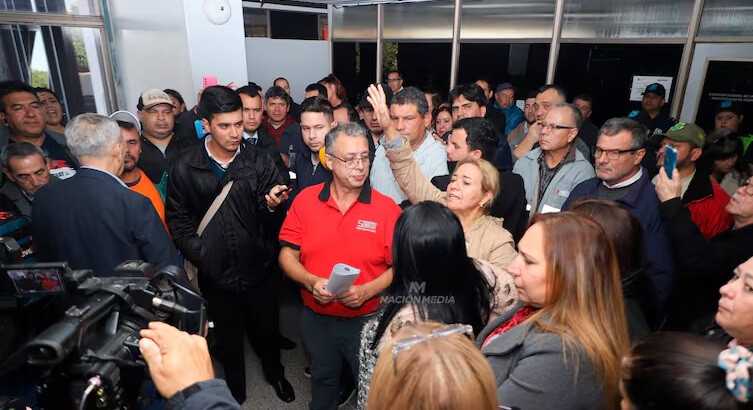
Asunción, Paraguay – With the recent approval of interventions in the municipal governments of Asunción and Ciudad del Este, attention has focused on the scope of the intervenor's authority. Constitutional experts have clearly stated that the intervenor's role is limited to maintaining administration and cannot involve personnel matters (hiring and firing) or political decisions. This measure is interpreted as an effort to prevent confusion and minimize administrative vacuums.
Background and Purpose of the Interventions
Municipal government intervention typically occurs in emergency situations, such as severe administrative corruption, financial problems, or a mayor's inability to perform their duties. The purpose is to prevent the paralysis of the respective municipal government, maintain normal administrative operations, and thoroughly investigate the cause of the problems.
Recently, the need for municipal government intervention became apparent as financial difficulties surfaced, including protests by Asunción city hall employees demanding overdue wages. Ciudad del Este is also known to have become subject to intervention due to similar administrative and financial issues. Such interventions are considered an unavoidable measure to ensure transparency and restore public trust.
Constitutional Expert Marcelo Duarte's View
Constitutional expert Attorney Marcelo Duarte explained the intervenor's authority in municipal government interventions as follows. He emphasized that the intervenor's role is "focused on decisions of an administrative nature" and that they "cannot make any decisions of a political nature." This means the intervenor must concentrate on continuing the municipal government's operations and preventing chaos in emergency situations.
Key Limitations on Authority:
No Personnel Authority: The intervenor cannot hire new employees or dismiss existing ones. This is to prevent permanent effects on the municipal government's workforce structure. Personnel matters fall under the authority of duly elected officials, such as the mayor and city council.
No Political Decisions: The intervenor cannot make political decisions, such as changing the municipal government's policy direction, enacting new ordinances, or approving major projects. Such decisions must be made through the legitimate procedures of elected officials.
Limited Financial Execution: The intervenor can execute budgets, but this is limited to essential expenditures for municipal government operations within the scope of the previously approved budget. They cannot pursue large-scale projects that incur new financial burdens or arbitrarily change budget items.
The Intervenor's Primary Role
Duarte summarized the intervenor's role as "verifying exactly what happened in the municipal administration." In other words, the intervenor focuses on thoroughly investigating the municipal government's financial status, contractual relationships, and administrative procedures, and identifying problems. This helps uncover the causes of corruption or mismanagement and collects information necessary for future improvement plans.
The detailed roles of the intervenor are as follows:
Administrative Maintenance: Manages the municipal government's daily administrative tasks to prevent interruptions. For example, they oversee civil complaint processing, public service provision, and essential administrative procedures.
Financial Status Assessment: Thoroughly investigates the municipal government's revenues and expenditures, and debt status to assess financial soundness.
Contract and Project Review: Reviews various contracts entered into by the municipal government and ongoing projects for any illegality or impropriety.
Problem Reporting: Documents in detail the problems found during the investigation and submits reports to superior bodies (e.g., the Ministry of Interior or Congress). These reports can serve as grounds for future impeachment of the mayor or for developing improvement plans.
Ensuring Transparency: Takes measures to enhance the transparency of municipal government operations and ensures citizens' access to information.
Limitations of Intervention and Future Challenges
Municipal government intervention is an effective tool for temporarily normalizing municipal functions and identifying problems in emergency situations. However, due to the limited authority of the intervenor, there may be limitations in resolving fundamental problems. For example, if there is a severe shortage of personnel or significant financial difficulties, intervention alone may not be sufficient to resolve them.
Ultimately, a new mayor must be elected, or the existing mayor must return to office, to establish and implement long-term plans for problem resolution. Furthermore, systematic improvements to strengthen the municipal government's financial soundness and enhance the integrity of public officials must continue.
These interventions in the municipal governments of Asunción and Ciudad del Este are expected to be an important turning point in strengthening the transparency and accountability of local governments in Paraguay. Significant changes are anticipated in the future administrative direction and financial management of these municipal governments based on the intervention results.
[Copyright (c) Global Economic Times. All Rights Reserved.]