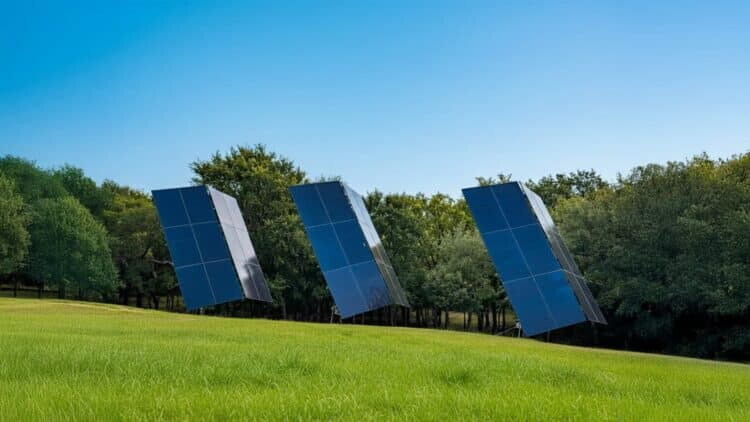
DALLAS, TX — A groundbreaking innovation originating from the United States is poised to fundamentally alter the landscape of renewable energy. Texas-based startup Janta Power, founded in 2021, has introduced modular 3D solar towers that promise to be up to three times more efficient per square meter than conventional flat solar panels, signaling a potential shift away from traditional solar farms.
The urgency of the global energy transition, driven by climate change and the depletion of fossil resources, has propelled solar energy into a prominent position. However, the spatial demands and fixed-tilt limitations of traditional photovoltaic arrays have created bottlenecks in densely populated and land-scarce areas. Janta Power's vertical, modular structures offer an elegant solution, optimizing available space and adapting seamlessly to challenging or limited terrains.
Efficiency and Versatility as Key Differentiators
The core strength of Janta Power’s technology lies in its vertically integrated design, which incorporates precise azimuthal solar tracking and integrated energy storage within the same mechanism. This allows the towers to follow the sun's path accurately throughout the day, maximizing energy capture and output. The company claims the system generates up to three times more power for the same land footprint and delivers approximately 50% more daily energy compared to two-dimensional solar technology.
This high power density makes the 3D solar towers ideal for industrial, commercial, and utility-scale implementation in settings where land is at a premium, such as urban centers, fragmented lots, parking lots, and rooftops. Investor MaC Venture Capital, which recently led a $5.5 million seed funding round for the company alongside Collab Capital, highlighted this advantage: "Their 3D solar tower technology delivers up to three times the efficiency of traditional solar panels while using a fraction of the footprint, making solar power scalable for more industries and communities around the world." The funding is earmarked to accelerate the commercial rollout and expand the company's global mission.
Airports Lead the Charge in Adoption
One of the first major sectors to recognize the enormous potential of Janta Power’s towers is the aviation industry. Airports present a unique energy challenge, characterized by high electricity demand, limited real estate for solar farms, and stringent restrictions concerning light reflection that could affect pilots.
The compact, low-reflection, and orientable nature of the 3D solar towers makes them a perfect fit. In a significant endorsement, Airports for Innovation (A4I), an international network dedicated to sustainable aviation solutions, selected Janta Power as the winner in the “Sustainable Aviation” category of its recent innovation contest. This recognition immediately secured a pilot deployment at Munich Airport, with plans for rollouts at other major international hubs in the network, including Dallas-Fort Worth (DFW), Dubai, Athens, and Vancouver. DFW Airport, located near Janta Power's Dallas Design District headquarters and operational lab, is reportedly preparing to launch its pilot program soon.
A Global Vision for Energy Access
Beyond the immediate commercial applications in the U.S. and Europe, Janta Power’s mission is deeply rooted in global energy access. Founder Mohammed Njie, originally from The Gambia, has leveraged his experience with unreliable electricity to design a solution for underserved communities. The company is already planning international projects, having previously spearheaded solar and energy storage initiatives in hospitals and schools in his home country.
As Janta Power moves from prototype validation into commercial deployment, the question for the solar industry remains: Is this the end of solar as we know it, or the beginning of a powerful, space-saving complement? By rewriting the rules of energy generation in a vertical, compact format, this U.S. innovation is decisively accelerating the transition to a sustainable and ubiquitous clean power future.
[Copyright (c) Global Economic Times. All Rights Reserved.]